| MCMD2 |
Format 1: regexlen(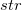 ,regular expression)
,regular expression)
Format 2: regexlenw(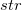 ,regular expression)
,regular expression)
Returns the length of substring where the defined regular expression matches the string 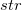 . The function returns 0 if no match is found, in other words, 0 character match.
. The function returns 0 if no match is found, in other words, 0 character match.
Use regexlenw function if 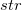 or regular expression contain multibyte characters.
or regular expression contain multibyte characters.
Find out the length of the longest substring that matches with the regular expression c.*a. Since the same input data is used for matching substring in the regexstr function, it is easier to compare the results.
$ more dat1.csv
id,str
1,xcbbbayy
2,xxcbaay
3,
4,bacabbca
$ mcal c='regexlen($s{str},"c.*a")' a=rsl i=dat1.csv o=rsl1.csv
#END# kgcal a=rsl c=regexlen($s{str},"c.*a") i=dat1.csv o=rsl1.csv
$ more rsl1.csv
id,str,rsl
1,xcbbbayy,5
2,xxcbaay,4
3,,0
4,bacabbca,6
Find out the length of the longest substring that matches "い.*あ". However, since regexlen function do not support multibyte character, it returns the number of bytes instead of number of characters.
$ more dat2.csv
id,str
1,漢漢あbbbいyy
2,漢あbいいy
3,
4,bあいあbbいあ
$ mcal c='regexlen($s{str},"あ.*い")' a=rsl i=dat2.csv o=rsl2.csv
#END# kgcal a=rsl c=regexlen($s{str},"あ.*い") i=dat2.csv o=rsl2.csv
$ more rsl2.csv
id,str,rsl
1,漢漢あbbbいyy,9
2,漢あbいいy,10
3,,0
4,bあいあbbいあ,14
Find out the length of the longest substring that matches "い.*あ". The regexlenw function is able to process multibyte characters to count the number of characters.
$ mcal c='regexlenw($s{str},"あ.*い")' a=rsl i=dat2.csv o=rsl3.csv
#END# kgcal a=rsl c=regexlenw($s{str},"あ.*い") i=dat2.csv o=rsl3.csv
$ more rsl3.csv
id,str,rsl
1,漢漢あbbbいyy,9
2,漢あbいいy,10
3,,0
4,bあいあbbいあ,14