| ZDD |
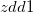 /
/ 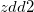
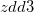
Compute the division of 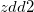 by
by 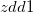 . Refer to the examples below for details.
. Refer to the examples below for details.
Division of valued sum of products x by constant c expressed in x/c, where the weight (density) of each term in x is divided by c.
> require 'zdd'
> a=ZDD::itemset("a")
> b=ZDD::itemset("b")
> x=13*a+3*b
> x.show
13 a + 3 b
# term a: quotient of 13/5 is 2 and thus becomes 2a. term b: quotient of 3/5 is 0 and
# thus not shown.
> (x/5).show
2 a
# term a: remainder of 13/5 is 3 and thus becomes 3a. term b: remainder of 3/5 is 3 and
# thus becomes 3b.
> (x%5).show
3 a + 3 b
# restore the original value of x by multiplying the quotient with the divisor 5 and
# adding the reminder.
> (5*(x/5)+(x%5)).show
13 a + 3 b
Division of valued sum of products x by itemset v expressed in x/v, where each term in x is divided by v.
Consider the operation is similar to a general polynomial.
> require 'zdd'
> a=ZDD::itemset("a")
> b=ZDD::itemset("b")
> c=ZDD::itemset("c")
> x=7*a*b+5*b*c
> y=7*a*b+5*b*c+2*c
> x.show
7 a b + 5 b c
> y.show
7 a b + 5 b c + 2 c
# quotient of 7ab/b is 7a. quotient of 5bc/b is 5c.
> (x/b).show
7 a + 5 c
# remainder of 7ab/b is 0. remainder of 5bc/b is 0.
> (x%b).show
0
# quotient of 7ab/3b is 2a. quotient of 5bc/3b is 1c. quotient of 2c/3b is 0 and thus not shown.
> (y/(3*b)).show
2 a + c
# remainder of 7ab/3b is ab. remainder of 5bc/3b is 2bc. remainder of 2c/3b is 2c.
> (y%(3*b)).show
a b + 2 b c + 2 c
# restore the original value of y by multiplying the quotient with the divisor 3b and
# adding the remainder.
> (3*b*(y/(3*b))+(y%(3*b))).show
7 a b + 5 b c + 2 c
Division of 2 valued sum of products x,y is computed as x/y.
Divisor y consists of multiple product terms 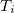 , find out
, find out 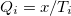 for all
for all  .
. 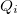 contains all common itemsets (terms), where Q is defined as the absolute minimum value weight of the terms.
contains all common itemsets (terms), where Q is defined as the absolute minimum value weight of the terms.
Note that this operation is different than general polynomial.
> require 'zdd'
> a=ZDD::itemset("a")
> b=ZDD::itemset("b")
> c=ZDD::itemset("c")
> d=ZDD::itemset("d")
> x=2*a*b+4*a*c+a*d-2*b*c+3*b*d
> y=a+b
> x.show
2 a b + 4 a c + a d - 2 b c + 3 b d
> y.show
a + b
# x/y and x%y are computed as follows.
# Q1=(x/a)=2b +4c +d +0 +0 = 0 +2b +4c +d
# Q2=(x/b)=2a +0 +0 -2c +3d = 2a +0 -2c +3d
# Common itemsets for Q1 and Q2 are c and d, the absolute minimum value is -2c and d.
# The quotient is derived as follows.
> (x/y).show
- 2 c + d
# compute x-(y*Q) to find out the remainder from the division of x%y.
> (x%y).show
2 a b + 6 a c + 2 b d
# Restore the original value of x by multiplying the quotient with the divisor y and
# adding the remainder.
> (y*(x/y)+(x%y)).show
2 a b + 4 a c + a d - 2 b c + 3 b d
% :Remainder operator
* : Multiplication operator