| MCMD2 |
Calculate the moving average. The three different ways to calculate moving average include simple moving average (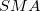 ), weighted moving average (
), weighted moving average (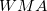 ), and exponential moving average (
), and exponential moving average (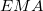 ).
).
The value of 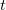 time is expressed by
time is expressed by 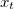 , and period is represented by
, and period is represented by 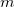 as defined in several formulas of moving average (3.1,3.2,3.3).
as defined in several formulas of moving average (3.1,3.2,3.3).
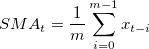 |
(3.1) |
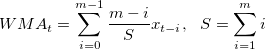 |
(3.2) |
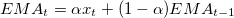 |
(3.3) |
mmvavg [s=] [k=] f= [t=] [-exp|-w] [alpha=] [skip=] [i=] [o=] [-nfn] [-nfno] [-x] [-q] [precision=] [--help] [--version]
s= After the specified field is sorted (multiple fields can be specified), moving average is calculated. s= parameter is required when -q option is not specified. k= Aggregate records using the specified field name(s) (multiple fields can as unit of calculation. f= Compute the moving averages of the field(s) (multiple fields can be specified). t= Interval numbers of integers greater than 1. When -exp is used with alpha=, the t= parameter do not need to be defined. -w Linear weighted moving average. -exp Exponential smoothing moving average. alpha= Use a real number as smoothing coefficient when -exp is specified. The default value of alpha is alpha=2/(value of = t+1)。 skip= Specify the number of rows to hide from the top in the output. Default value: skip=(value of t= -1), skip=0 when -exp is specified.
The first row is not printed as there is less than the number of required intervals for computation.
$ more dat1.csv id,value 1,5 2,1 3,3 4,4 5,4 6,6 7,1 8,4 9,7 $ mmvavg s=id f=value t=2 i=dat1.csv o=rsl1.csv #END# kgmvavg f=value i=dat1.csv o=rsl1.csv s=id t=2 $ more rsl1.csv id%0,value 2,3 3,2 4,3.5 5,4 6,5 7,3.5 8,2.5 9,5.5
The first row is not printed as there is less than the number of required intervals for computation.
$ mmvavg s=id f=value t=2 -w i=dat1.csv o=rsl2.csv #END# kgmvavg -w f=value i=dat1.csv o=rsl2.csv s=id t=2 $ more rsl2.csv id%0,value 2,2.333333333 3,2.333333333 4,3.666666667 5,4 6,5.333333333 7,2.666666667 8,3 9,6
Exponential smoothing moving average (-exp) includes the first row in the output.
$ mmvavg s=id f=value t=2 -exp i=dat1.csv o=rsl3.csv #END# kgmvavg -exp f=value i=dat1.csv o=rsl3.csv s=id t=2 $ more rsl3.csv id%0,value 1,5 2,2.333333333 3,2.777777778 4,3.592592593 5,3.864197531 6,5.288065844 7,2.429355281 8,3.47645176 9,5.82548392
$ more dat2.csv id,key,value 1,a,5 2,a,1 3,a,3 4,a,4 5,a,4 6,b,6 7,b,1 8,b,4 9,b,7 $ mmvavg s=key,id k=key f=value t=2 i=dat2.csv o=rsl4.csv #END# kgmvavg f=value i=dat2.csv k=key o=rsl4.csv s=key,id t=2 $ more rsl4.csv id,key,value 2,a,3 3,a,2 4,a,3.5 5,a,4 7,b,3.5 8,b,2.5 9,b,5.5
$ more dat3.csv key,value a,1 a,2 a,3 a,4 a,5 b,6 b,1 b,4 b,7 $ mmvavg -q k=key f=value t=2 skip=0 i=dat3.csv o=rsl5.csv #END# kgmvavg -q f=value i=dat3.csv k=key o=rsl5.csv skip=0 t=2 $ more rsl5.csv key,value a,1 a,1.5 a,2.5 a,3.5 a,4.5 b,6 b,3.5 b,2.5 b,5.5
mmvstats : Specify the average as well as various types of statistics.
mmvsim : Compute bivariate statistics.
mwindow : Computes statistics on sliding window data which cannot be computed using mmvstats.